Educational Perspective of the PPR Potential Based Cohesive Model
The PPR UELs in 2D and 3D, based on the Engineering Fracture Mechanics journal papers below, are available for download on this page.
"Computational implementation of the PPR potential-based cohesive model in ABAQUS: Educational perspective." K. Park and G.H. Paulino. Engineering Fracture Mechanics. Vol. 93, pp. 239-262, 2012.
Link to PDF
"A growing library of three-dimensional cohesive elements for use in ABAQUS." D. Spring and G.H. Paulino. Engineering Fracture Mechanics. Vol. 126, pp. 190-216, 2014.
Link to PDF
Jump to section:
The flowchart to the left shows the major steps of the PPR UEL, which is available below. The subroutine is entered and exited from the ABAQUS finite element routine at the green ellipses.
Downloads:
2D UEL (zip format)
3D BRICK UEL (zip format)
3D TET4 UEL (zip format)
3D TET10 UEL (3D) (zip format)
Additional PPR Resources:
- Nomenclature (equivalence between variables in paper and in UEL)

Flow chart of the PPR UEL
ABAQUS analysis using the PPR UEL is shown below for the mixed-mode bending test. The domain is discretized by bilinear quadrilateral elements
(Q4), and cohesive elements are inserted along the horizontal direction, which corresponds
to the potential crack path, i.e. the intrinsic cohesive zone model. The analytical solution is available for 3 stages and is compared to the results obtained with the PPR model below.
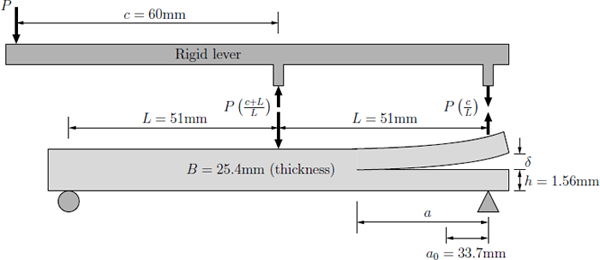

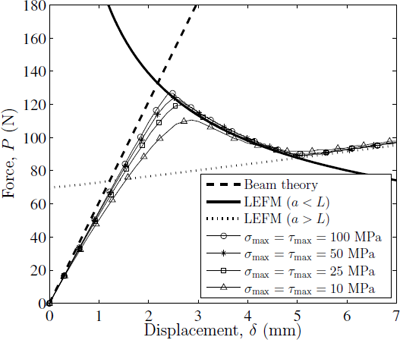
The ABAQUS input file representing the problem above is available for download below. The file contains the relevant information pertaining to the mesh (nodes and element connectivity), material properties for the bulk and cohesive elements, and loads and boundary conditions, etc.
Download input file (2D)
Download input file (3D)
The results shown in the figure to the right can be obtained using a simple Matlab script that parses the relevant information from the ABAQUS output file (*.dat) and plots the result.
Download MatLab parser/plotter
Download input file (2D)
Download input file (3D)
The results shown in the figure to the right can be obtained using a simple Matlab script that parses the relevant information from the ABAQUS output file (*.dat) and plots the result.
Download MatLab parser/plotter
The following example is that of a single coated particle imbedded in an elastic matrix. The model considers a single octant of the particle, with symmetric boundary conditions, as illustrated in the Figure. The particle has a radius of 1 mm, the coating has a thickness of 0.2 mm, and the particle volume fraction is 40%. Linear, eight-node brick (B8) elements are used to discretize the domain. Approximately 150,000 elements discretize the bulk domain, while 3230 cohesive elements are inserted between the coating and the bulk matrix to account for the debonding behavior.
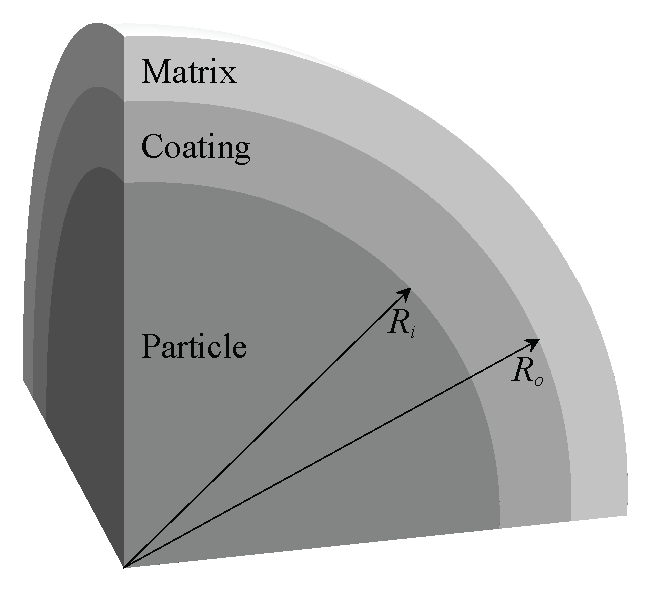
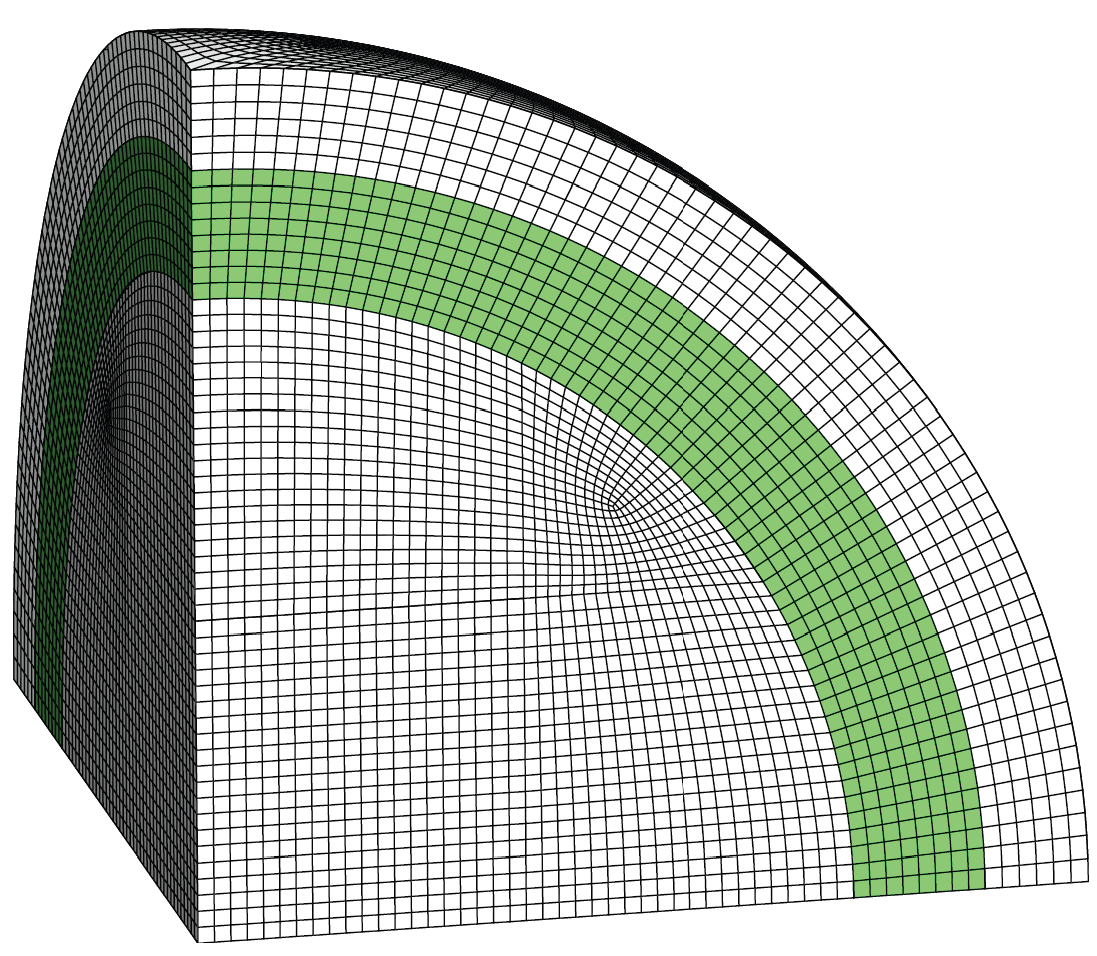


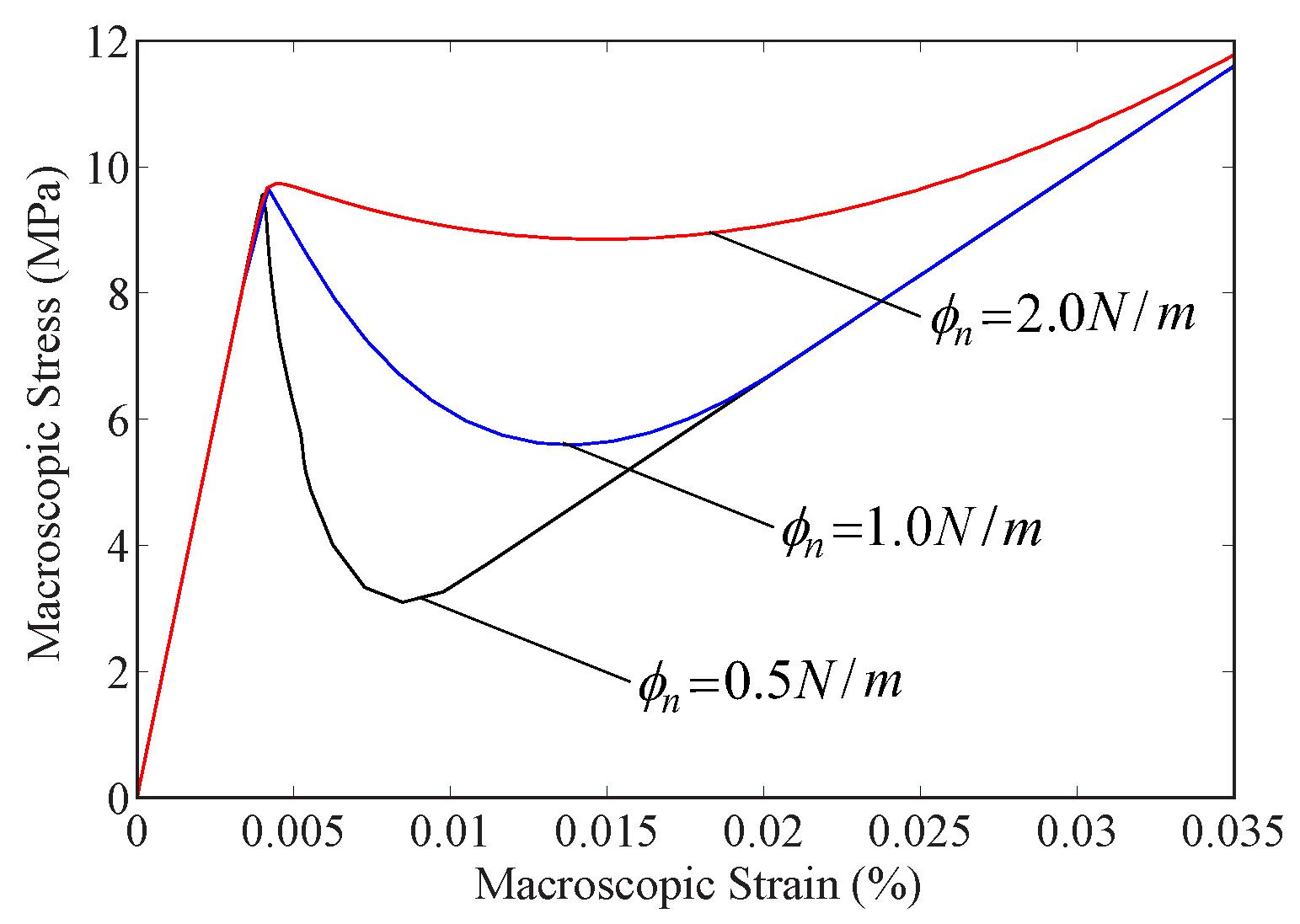
The ABAQUS input file representing the problem above is available for download below. The file contains the relevant information pertaining to the mesh (nodes and element connectivity), material properties for the bulk and cohesive elements, and loads and boundary conditions, etc.
Download input file (3D)
The results shown in the figure to the left can be obtained using a simple Matlab script that parses the relevant information from the ABAQUS output file (*.dat) and plots the result.
Download MatLab parser/plotter

